Colorado Wildlife Experts Tracking Spread Of Deadly Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease
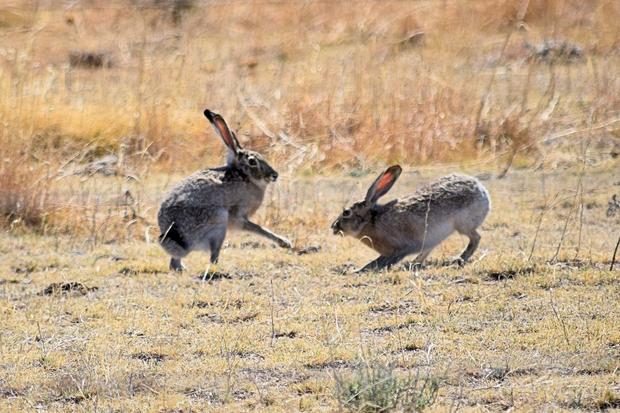
DENVER (CBS4) -- Wildlife managers across Colorado are closely monitoring a highly contagious and deadly disease that they say could significantly impact the rabbit population in the state -- and the predators that rely on them. It's called Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus type 2 (RHDV-2).
The most recent case was in Adams County, in the area around Karen Swaithes' home.
"The jackrabbits around here have a tendency to eat the bark off our trees and we have, and they are very plentiful," she said.
Despite them being a nuisance at times, Swaithes says it was a concern when her family started to notice several were dying off.
"As the days progressed, we were seeing more of them dead and we thought this was really strange," Swaithes said.
Her daughter called Colorado Parks and Wildlife who immediately came to inspect the dead animals, later determining that they were infected with Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease.
"It's in seven counties right now in Colorado, the first time ever seeing those detection. It's in jackrabbits, cottontails and domestic breeds, so it is one thing that we need to monitor," CPW spokesperson Jason Clay said.
RELATED: Rabbits In Adams County Test Positive For Deadly Disease RHDV-2
Clay says the disease, while highly contagious, only effects rabbits -- not humans or other pets.
He says any impact to the population, however, could harm a variety of other animals.
"A lot of the other predator mammals -- your coyotes, foxes, bobcats some of your owls and hawks -- can feed on rabbits. Snakes can feed on rabbits. There are a lot of species that rely on them," Clay said.
Because it is considered a foreign disease coming to North America from Europe he says both state and Federal wildlife officials will be monitoring the spread closely.
"The more people can help with observations of what they may or may not be seeing help reporting that can help us get an idea where the disease is going.
The other six in Colorado with positive RHDV-2 cases are Alamosa (wild cottontail and jackrabbits), El Paso (feral rabbits, wild jackrabbits and domestic rabbit), Montezuma (domestic rabbit), Prowers (wild cottontails), Pueblo (wild cottontails) and Weld (domestic rabbit).
RHDV-2 can cause internal bleeding and swelling, according to wildlife officials. Affected animals may have blood staining the nose and mouth.
For more information on the disease and its impact to domestic rabbits or information on how to report visit cpw.state.co.us/Documents/Wildlife-Health/Rabbit_Hemorrhagic_Disease.pdf